What is IaaS in Cloud Computing
In this article we will understand what is Infrastructure as a Service also called IaaS. In addition to Infrastructure as a Service, we also have Platform as a Service (also called PaaS) and Software as a Service (also called SaaS). Up until recently, these are the 3 main cloud services offered by most cloud service providers.
With cloud technologies advancing and maturing so fast, in addition to these 3 cloud offerings, we also have
- Containers as a Service (CaaS)
- Functions as a Services (FaaS or Serverless Computing)
In this article, let's understand, what is Infrastructure as a Service. Who use this service and the benefits it provide.
On premise data center
If we are not using cloud, we manage everything on-premise. Basically our organisation is responsible for managing pretty much everything.
- Procuring physical servers, storage and related hardware
- Install and set up the network
- Setting up the server room or data center
- Make sure there is main power supply, back-up power supply, cooling system etc are in place
- Install and configure virtualization software, operating system, any middleware or runtime components that your software developement or other teams need.
- Install, configure, and manage your custom or packaged apps and data.
So the point is, with on-premise data center, our organisation is reponsible for managing pretty much everything.
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
As the name implies, with Infrastructure as a Service, you rent or lease IT infrastructure from a cloud service provider like Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services or some other cloud provider. To understand this better, take a look at the following diagram.
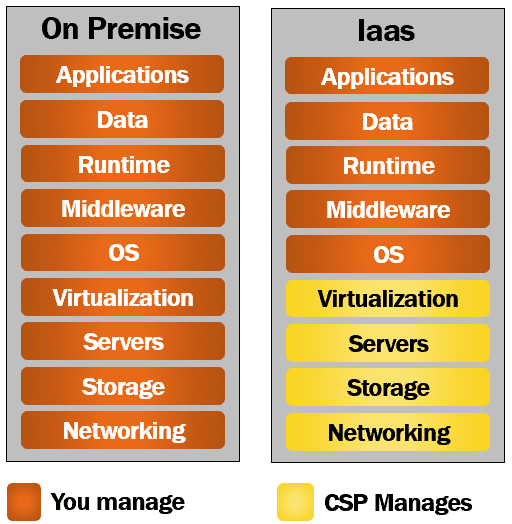
As the name implies, with Infrastructure as a Service, the cloud service provider provides the infrastructure over an internet connection or through a virtual private network. We will discuss what a virtual private network is in our upcoming articles. For now, you can think of it as a dedicated and secure private tunnel between you (i.e your organization) and the cloud service provider.
So the important point to keep in mind here is, there is no need for your organization to procure and manage the infrastructure. It is the cloud service provider that is responsible for
- Procuring physical servers, storage and related hardware
- Install and set up the network
- Make sure there is proper power supply, back-up power supply, cooling system etc are in place
- Pretty much the cloud service provider is responsible for setting up, securing and managing the cloud data center.
So in simple terms, this is how it works. The cloud service provider hosts the infrastructure at their data center. You as a customer, provision this infrastructure on-demand over the internet or through a virtual private connection. For the duration that you use the infrastructure, you pay a fee. You are only charged based on the number of machines and resources that are actually being used.
As you can see from the image, all the yellow boxes, i.e networking, storage, servers and virtualization are managed by the cloud service provider. The rest (i.e OS, Middleware, Runtime, Data and Application) are still managed by you.
This means you have better control and you can install any operating system of your choice, windows or linux for example. So the point is, you can use this infrastructure for anything you want. Computational or storage needs. May be, you have a web application which, you can host and run for example. You can also use it for your storage needs. For example, install SQL Server, Oracle or some other relational database and store your relational data. I mean, a diverse set of use cases are supported. Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is also known as hardware as a service (HaaS).
Who uses Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
In most organisations, it is the Infrastructure team that procures servers, and computers. Install software and provide systems to employees. Set up and manage networks. So in most cases, it is usually your infrastructure team that uses Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). Sometimes, even software developments teams use this service if they want to have enhanced control over the underlying hardware and network.
Benefits of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Reduced financial risk
There is a reduced financial risk for organisations. Let's say, for example, you want to try something new (may be you are launching a new business or product line or experimenting something entirely new) and for that you need a software application. To host and run this application you need a server, all the related infrastructure and workforce to setup and maintain. What if your new product launch or experiment fails. You have already spent a fortune to purchase the server and related infrastructure.
With the Infrastructure as a Service, you pay a fee, for as long as you use the cloud infrastructure. Host your app and run it from there. If your new product launch or experiment succeeds, well and good. If it doesn't shut things down and you pay no longer. Straight away, you can see how organisations can benefit from the reduced financial risk. This encourages businesses to try new things, experiment and innovate more.
Deployment Speed
Just imagine the time it takes to procure physical servers, storage and the related infrastructure. You need to purchase. Get them shipped over. Create a server room or data center. Secure it. Install power supply and cooling systems. Setup and configure network. The list goes on. You also need to hire skilled people to do all these. It takes a considerable amount of time to have all these in place. Probably days, sometimes even months in worst case scenarios.
On the other hand, if you are using, Infrastructure as a Service, you point your browser to the cloud service provider web portal, and with a few clicks in just a few minutes you have one or many virtual machines procured. So you can see the speed with which we can procure and start using cloud infrastructure. So you really get time to focus on what matters to your business.
Provision resources from geographically closer locations
Cloud service providers, for example, Amazon, Microsoft and Google, have data centers all over the world. This means, with the Infrastructure as a Service, you have the option of provisioning the servers from geographic locations close to your customers.
Unlimited scalability
You almost will never run out of resources in a public cloud. It provides near unlimited scalability. You can set threshold limits to automatically scale up and down depending on the demand.
© 2020 Pragimtech. All Rights Reserved.

