What is a public cloud. Benefits, limitations and use cases
There are different types of clouds.
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
In this article we will understand, what is a public cloud, benefits, limitations and use cases. In our next articles we will learn about Private and Hybrid cloud.
What is a public cloud
As the name implies, a public cloud is public and is the most common type of cloud. It is easy for anyone i.e an individual or an organisation to start using public cloud resources and services. There is no upfront huge capital expenditure. You don't have to buy the expensive hardware or worry about set up and maintaining the cloud. This is because, with the public cloud, all the infrastructure (i.e the physical servers, storage, networking etc) are procured and owned by the cloud service provider. It is this cloud service provider, that sets up the cloud and maintains it there on. Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services are examples of a public cloud.
We access public cloud resources and services over the internet. So to use a public cloud, we need an internet connection and manage the cloud services and resources through a web portal provided by the cloud service provider. For the cloud services and resources we use, we pay a monthly fee to the public cloud service provider. This monthly fee is like your utility bills, water or electricity for example. It's pay as you go model, meaning you pay for what you use.
Anyone can use the public cloud. In a public cloud, your organisation share the same hardware, storage and network devices with other organisations. In cloud computing terms, this is called multi-tenancy. Your organisation data may be stored along with other organisations data on the same storage device.
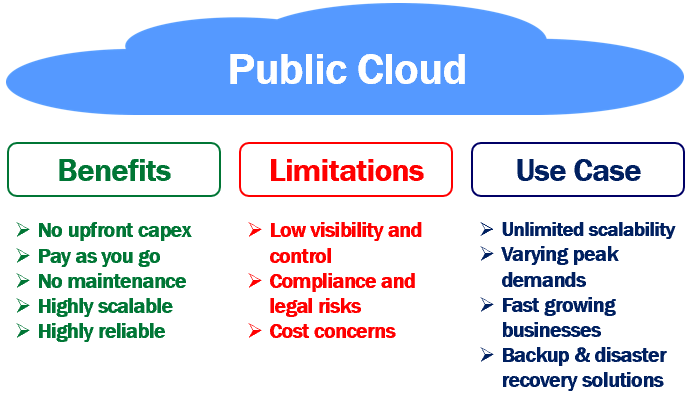
Benefits of public cloud
- You don't have to buy expensive hardware or set up your own datacenter i.e no upfront capital expenditure.
- It supports pay as you go model. You only pay for what you use, just like your water, or electricity monthly bills.
- No maintenance headaches. You as a consumer, don't have to worry about maintaining the public cloud i.e replacing the failed hardware, installing the security patches, updates etc. Your service provider is responsible for maintaining the public cloud. You only pay a small monthly fee, based on the cloud services you use.
- Highly scalable. You will almost never run out of resources in a public cloud. Based on your business needs you can scale resources up and down. You can even automate this by setting threshold limits.
- Highly reliable. A public clous is a vast network of servers. So data, is always backed up. This means hardware failure, power failure, natural disaster or other crisis do not result in data loss. So, bottom line, public cloud is highly reliable.
Limitations of public cloud
- Low visibility and control - Public cloud infrastructure is owned by the cloud service provider. You don't have much visibility and control over it.
- Compliance and legal risks - Since you don't have much visibility and control over public cloud infrastructure, you are relying on the cloud service provider to protect data and adhere to local and international regulations. Your company may still be liable, if the cloud service provider, fails to live up to the task and if there is a data breach. So a public cloud, may not be the most viable solution for security sensitive or mission-critical applications.
- Cost concerns - Cloud in general, reduces upfront infrastructure costs and it's pay-as-you-go model provides more flexibility. Depending on the traffic, the amount of cloud resources you consume, the plan you have chosen, the way you scale resources up and down, determines the overall price you pay. Sometimes this overall price tag may be higher than what you anticipated.
When to use public cloud
- We never run out of resources in a public cloud. It provides near-unlimited scalability. So, if you want to dynamically scale up and down at will, then public cloud is your solution.
- Businesses with varying peak demands greatly benefit from the public cloud. When there is high demand you scale up and when the demand subsides, you scale down and pay only for what you use.
- Fast growing businesses also greatly benefit from the public cloud. They can use the public cloud and quickly scale up operations rather than having to build your own private cloud which not only has huge upfront capital expenditure but also time consuming.
- Businesses can also benefit from the public cloud by using it for backup and disaster recovery solutions.
© 2020 Pragimtech. All Rights Reserved.

