What is a private cloud. Benefits, limitations and use cases
In this article we will understand, what is a private cloud, benefits, limitations and use cases. In our next articles we will learn about Hybrid cloud.
What is a private cloud
As the name implies, a private cloud is private to one organisation. In other words, a private cloud resources and services are used exclusively by one business or organisation. Unlike public cloud, a private cloud resources are not shared by multiple organisations. All the hardware infrastructure and software are solely dedicated to one organisation.
The private cloud is physically located on-premise i.e at your organisation’s on-site data centre, or it can also be hosted by a third-party service provider. The important point to keep in mind is, a private cloud is private, i.e all the hardware infrastructure and software are solely dedicated to one and only one organisation.
In a private cloud, it's very easy to customise the hardware and software to meet your oragnisation's specific IT requirements. This is because your organisation, owns everything i.e the hardware, software and network. So you have complete control and can change anything in any way you want to meet your organisation requirements.
In general, private clouds are often used by government agencies, financial institutions and any other medium to large-sized organisations with business-critical operations seeking enhanced control over their environment.
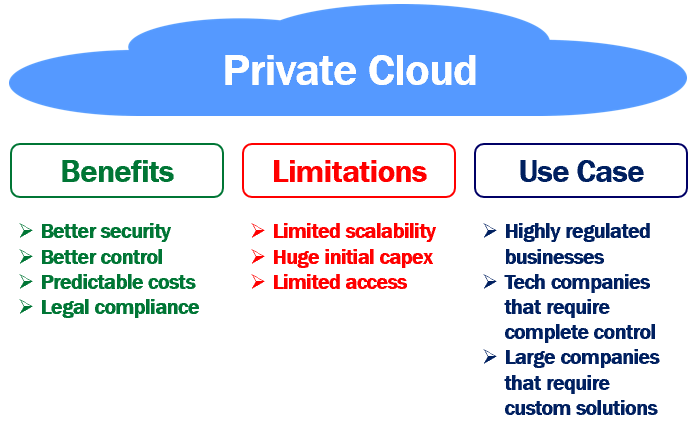
Benefits of private cloud
- Better security - Resources are not shared with other organisations, so there is better security with private cloud.
- Better control - A private cloud belongs to a specific organisation, so you can customise it to meet your specific business needs.
- Predictable costs - With private cloud you own all the cloud infrastructure and you are not paying any third party cloud service provider. So your monthly cooling, energy and maintenance costs are usually predictable.
- Legal compliance - When you deal with regulated data, for example, financial, health care or credit card data, there are strict rules around where the data is stored, who can handle and process it and how it is protected. With the private cloud you know where you data center is located. So you know where the data is stored and how it is protected.
Limitations of private cloud
- Limited scalability - The extent to which you can scale up in a private cloud is limited by the amount of infrastructure you have. Beyond certain point, you cannot scale up. So, the infrastructure is a limiting factor and you may not be able to scale up at will like in the public cloud, to meet unpredictable demands.
- Huge initial capital expenditure - With the private cloud you have to procure all the cloud infrastructure. Hire the workforce to set up and maintain the cloud. So a private cloud, is an expensive solution compared to public cloud alternatives especially for short-term projects.
- Limited access - A private cloud is usually more secure. We use it for security sensitive applications. Because of these high security measures in place, mobile users may have limited access to the private cloud outside of the corporate network.
When to use a private cloud
- Private cloud is best suited for highly regulated businesses like financial and healthcare institutions.
- Tech companies that require robust security and complete control over the cloud infrastructure also benefit from the private cloud.
- Large organisations that require advanced and custom data centre solutions also benefit from private cloud.
© 2020 Pragimtech. All Rights Reserved.

