ASP.NET Core REST API DbContext
In this video we will discuss adding database support for ASP.NET Core REST API service. For this we are going to use Entity Framework Core.
What is Entity Framework Core
Entity Framework Core is an ORM (i.e an Object-Relational Mapper). It's a complete rewrite from the ground up. If you have any experience with previous versions of Entity Framework, you will find lot of familiar features.
EF core is lightweight, extensible, and open source software. Like .NET Core, EF Core is also cross platform. It works on windows, Mac OS, and Linux. EF core is Microsoft’s official data access platform.
Entity Framework Core DbContext class
One of the very important classes in Entity Framework Core is the DbContext class. This is the class that we use in our application code to interact with the underlying database. It is this class that manages the database connection and is used to retrieve and save data in the database.
To use the DbContext class in our application
- We create a class that derives from the DbContext class.
- DbContext class is in Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore namespace.
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{ }DbContextOptions in Entity Framework Core
For the DbContext class to be able to do any useful work, it needs an instance of the DbContextOptions class.
The DbContextOptions instance carries configuration information such as the connection string, database provider to use etc.
We pass the DbContextOptions to the base DbContext class constructor using the base keyword as shown below.
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
}Entity Framework Core DbSet
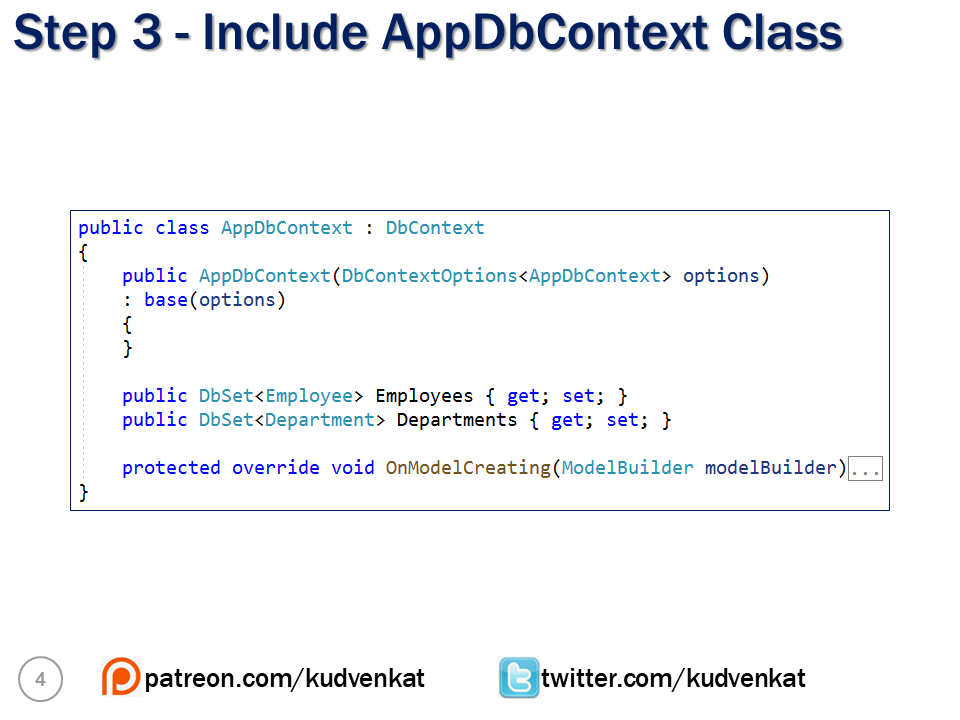
- The DbContext class includes a DbSet<TEntity> property for each entity in the model.
- At the moment in our application we have, 2 entity classes - Employee and Department.
- So in our AppDbContext class we have 2 corresponding DbSet properties.
DbSet<Employee>
DbSet<Department>- We will use these DbSet properties to query and save instances of Employee and Department classes.
- The LINQ queries against the DbSet properties will be translated into queries against the underlying database.
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
public DbSet<Department> Employees { get; set; }
}Seeding Data
Override OnModelCreating method to seed Employee and Department data.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
// Code to seed data
}AppDbContext class complete code
Create Models folder and include the following AppDbContext class in it.
using EmployeeManagement.Models;
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using System;
namespace EmployeeManagement.Api.Models
{
public class AppDbContext : DbContext
{
public AppDbContext(DbContextOptions<AppDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
public DbSet<Department> Departments { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(modelBuilder);
//Seed Departments Table
modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().HasData(
new Department { DepartmentId = 1, DepartmentName = "IT" });
modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().HasData(
new Department { DepartmentId = 2, DepartmentName = "HR" });
modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().HasData(
new Department { DepartmentId = 3, DepartmentName = "Payroll" });
modelBuilder.Entity<Department>().HasData(
new Department { DepartmentId = 4, DepartmentName = "Admin" });
// Seed Employee Table
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().HasData(new Employee
{
EmployeeId = 1,
FirstName = "John",
LastName = "Hastings",
Email = "David@pragimtech.com",
DateOfBrith = new DateTime(1980, 10, 5),
Gender = Gender.Male,
DepartmentId = 1,
PhotoPath = "images/john.png"
});
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().HasData(new Employee
{
EmployeeId = 2,
FirstName = "Sam",
LastName = "Galloway",
Email = "Sam@pragimtech.com",
DateOfBrith = new DateTime(1981, 12, 22),
Gender = Gender.Male,
DepartmentId = 2,
PhotoPath = "images/sam.jpg"
});
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().HasData(new Employee
{
EmployeeId = 3,
FirstName = "Mary",
LastName = "Smith",
Email = "mary@pragimtech.com",
DateOfBrith = new DateTime(1979, 11, 11),
Gender = Gender.Female,
DepartmentId = 1,
PhotoPath = "images/mary.png"
});
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>().HasData(new Employee
{
EmployeeId = 4,
FirstName = "Sara",
LastName = "Longway",
Email = "sara@pragimtech.com",
DateOfBrith = new DateTime(1982, 9, 23),
Gender = Gender.Female,
DepartmentId = 3,
PhotoPath = "images/sara.png"
});
}
}
}Install required NuGet packages
Install the following 2 NuGet packages.
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer
- Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools
Database Connection String
Include the following database connection string in appsettings.json file of the REST API project.
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DBConnection": "server=(localdb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;database=EmployeeDB;Trusted_Connection=true"
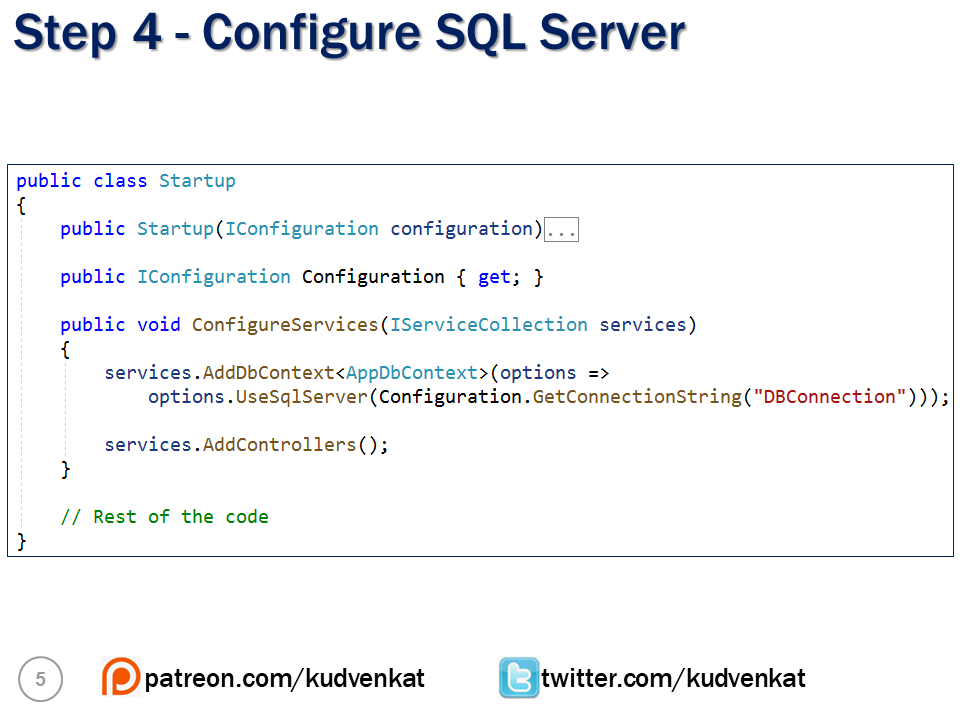
}ConfigureServices in API project Startup class
Read the connection string from appsettings.json file
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(Configuration.GetConnectionString("DBConnection")));
services.AddControllers();
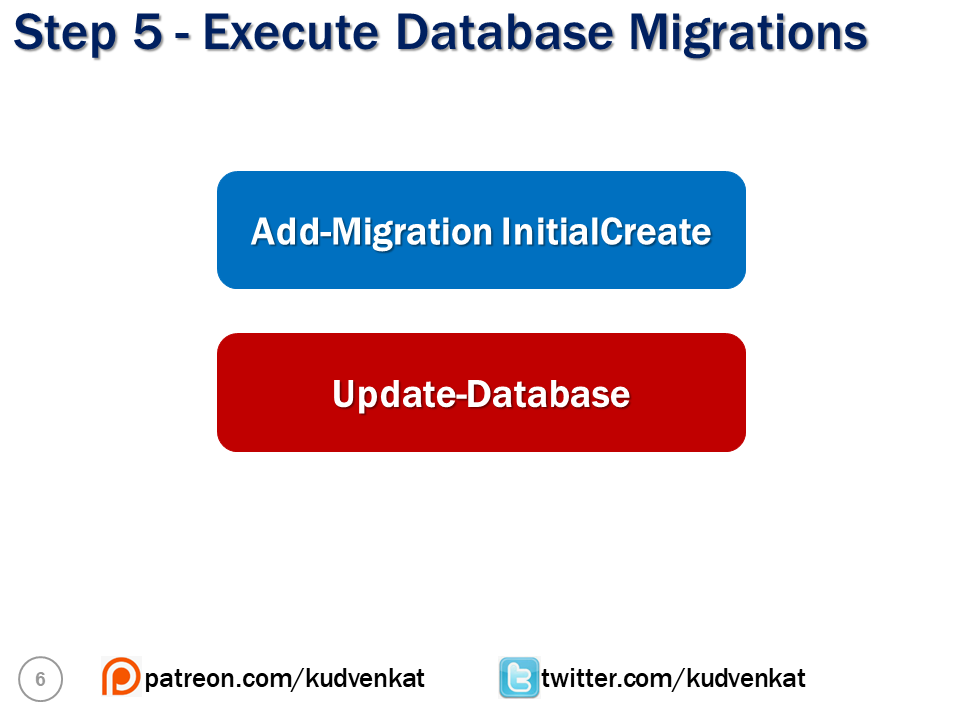
}Create and execute database migrations
Use the following 2 commands to create and execute the initial database migration
- Add-Migration InitialCreate
- Update-Database


© 2020 Pragimtech. All Rights Reserved.

